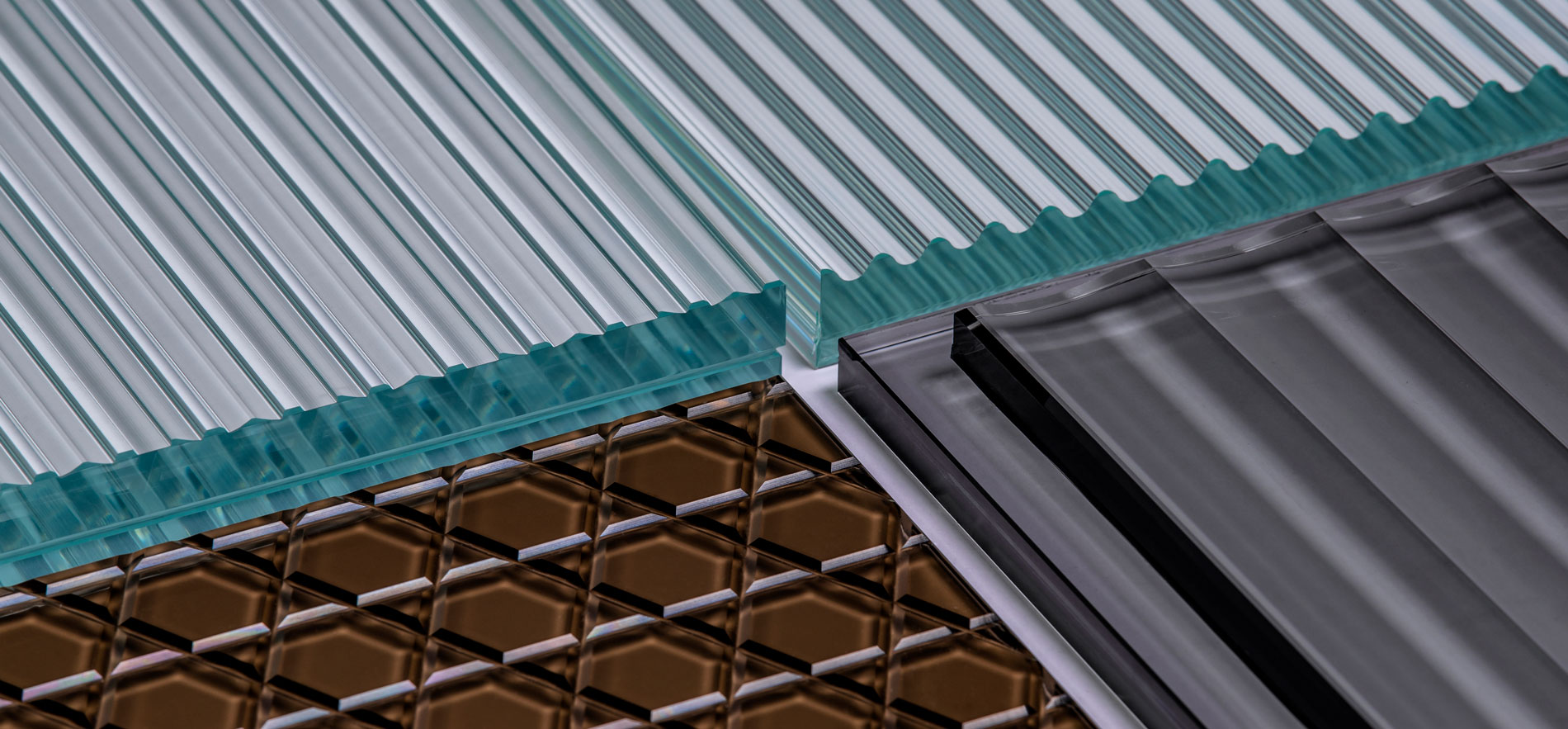
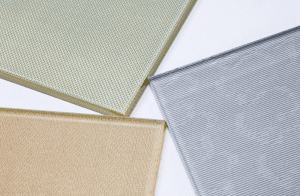
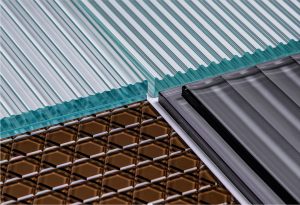
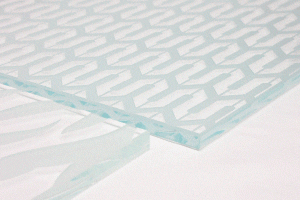
The choice of glass for architecture depends on specific applications, use cases, and your desired outcomes. Each type of architectural glass offers unique benefits and purposes, so several factors should be considered when selecting the optimal glass thickness.
Thicker glass provides increased strength, pronounced edges, and better resistance to bowing or warping under stress. However, it is heavier and more expensive compared to thinner glass, which may not be suitable for all projects. Lighter and thinner glass serves as a preferred alternative, and it can be seamlessly integrated with other construction materials such as wood and aluminum.
Ultimately, the best glass for architecture depends on the specific requirements and goals of your project. Consider factors such as cost, weight, strength, and compatibility with other materials when making the selection.